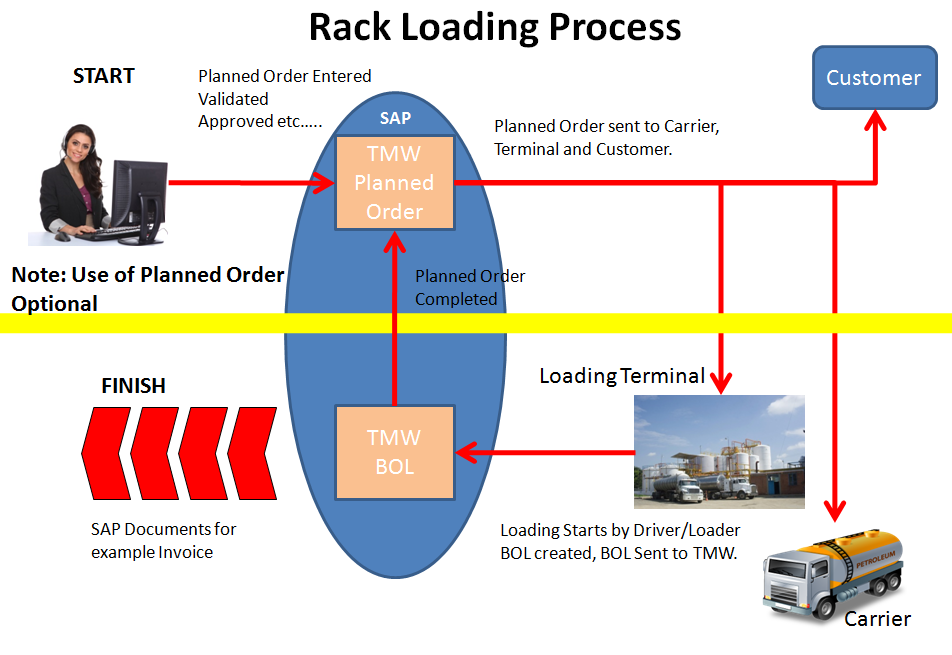
The following diagram explains the loading process with or without the use of planned orders. Planned orders are used when there is a need to pre-plan the load in advance, this common for Lubricants, Asphalt and Chemicals. The Planned Order is created based on a customer phone call, email or other means of communication. The planned order is communicated typical to the following parties:
- Loading Terminal
- Customer
- Carrier
TMW provides a complete to solution to manage planned orders in SAP from START to FINISH.
Loading start by the driver or the loader interfacing with local automation system (TAS- Terminal Automation System) in one of 3 ways:
- By entering planned order number OR
- By number a customer (consignee) number
- By entering deal number
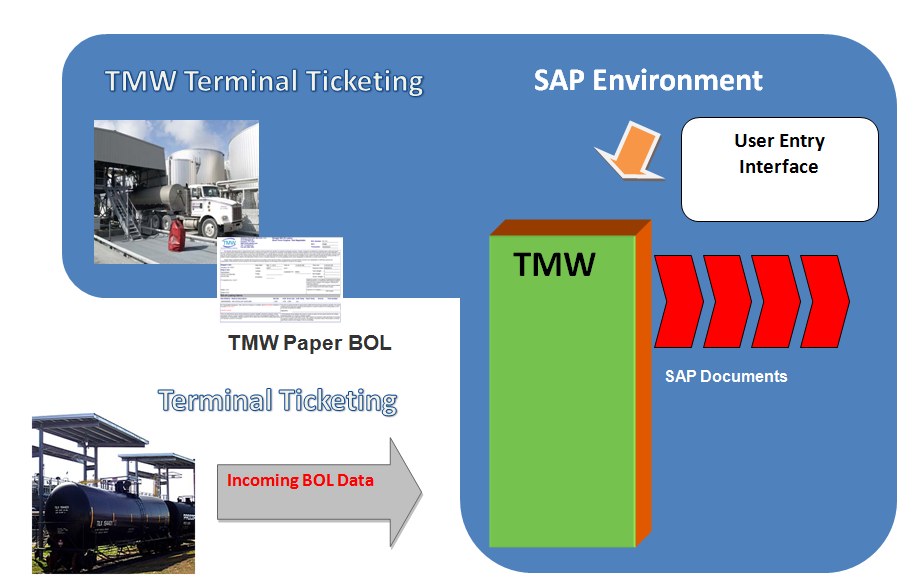
Note: TMW can be used as the local automation system (TAS) within the SAP environment.
Once loading is complete, a BOL is created and given to the driver and communicated to TMW automatically for customer billing.